Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is the most frequent cause of new blindness in 20-74 year-olds. There are approximately 21 million diabetics in the U.S. with 8 million having some form of diabetic retinopathy. Of those 8 million, 700,000 have serious retinal disease. There will be 65,000 new cases of proliferative diabetic retinopathy each year with 24,000 new cases of blindness.
The longer someone has diabetes, the increased risk of developing serious eye disease. After 15 years of diabetes, approximately 65% of patients not taking insulin and 85% of patients taking insulin will develop some form of diabetic eye disease.
Causes
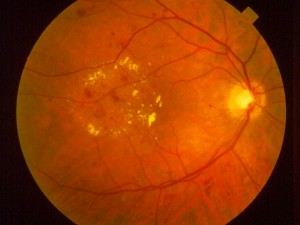
The small blood vessels in the retina become damaged from the high blood sugars in the circulation. The retina becomes ischemic (a decrease in blood flow to the retina). The ischemic retina sends out signals for the eye to produce new blood vessels to increase circulation. These new blood vessels are weak and can leak fluids and cause bleeding.
If abnormal blood vessels grow around the pupil, this can block fluid in the eye increasing pressure, causing glaucoma. Leaking blood can cloud the jelly-like vitreous inside the eye and block light entering the eye. New blood vessels can cause scar tissue that can pull the retina away from the back of the eye, causing a retinal detachment. Severe vision loss or blindness can result.
Symptoms
Diabetes can affect vision by causing an increased risk of cataracts and glaucoma. Also, high blood pressure and high cholesterol can aggravate diabetic retinopathy and retinopathy can progress very quickly during pregnancy. Common symptoms can be blurry or distorted vision, difficulty reading, sudden vision loss in one eye, halos around lights, dark spots or floaters in vision, or flashes of light.
Many people with vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy have no symptoms. This is why regular eye exams are so crucial.
Regular and complete eye exams are of the utmost importance for protecting your vision from diabetes and other eye problems.
To schedule your eye exam or learn more about your diabetes treatment options at Ohio Eye Alliance, please call us today at
Diagnosis
At Ohio Eye Alliance, we offer patients the most advanced technology available today for detecting and treating diabetic eye conditions. We tailor treatment therapy to each individual. This includes the use of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), a non-invasive means of obtaining cross-sectional, layered images of the retina. We also offer a complete retinal angiography department, which takes retinal photographs of the eye to detect signs of new blood vessel growth.
Treatment
preserved.